Introduction to Multimedia Storytelling
Marshal McLuhan: Medium is the Message
A quick motion graphics explainer that sums up McLuhan’s “medium is the message” in a visually engaging way.
Below, a more in-depth series based on an interview McLuhan did in 1977.
- Part 1 of 1977 Lecture on McLuhan’s Medium is the Message
- Part 2 of 1977 Lecture on McLuhan’s Medium is the Message
- Part 3 of 1977 Lecture on McLuhan’s Medium is the Message
And lastly, read this 2000 article from New York Times on what became of Marshall McLuhan after his passing.
Lean Forward vs Lean Back
 |
 |
| Illustrations by Gan Khoon Lay and Krisada of The Noun Project. | |
Lean Forward and Lean back describe a mode of consumption when using technological devices. These phrases describe the physicality of how a person is consuming media through a device, like a computers, television, book, or magazine. But more importantly, they describe how this type of consumption the affects the person consuming media — their attention span, their intent, and the methods they use to interact with the medium.
Lean Forward
Lean forward devices are laptops with keyboards or desktop computers. These are traditional devices of work, and as such, influence a person to perform and accomplish tasks. People traditionally use computers for work, e-mail, research, banking, and multitasking first, and leisure secondarily.
The affects on the brain are well documented, and generally a lean forward device affects a person in several ways:
- Scanning Mode People scroll and scan web pages rather than reading long bodies of text. They are in a frantic search mode, looking for bits of text, buttons, images, or anything to accomplish some kind of task.
- Frenetic People are on web pages for mere seconds, before clicking on links to go to another page. They are also impatient, especially when it comes to slowly loading web pages. Most users can discern a difference in page load time of 20 milliseconds.
- Shorter Attention Span People don’t stick around on web pages for long periods of time. They watch only a few seconds of a video; maybe several minutes if it’s compelling. There is a challenge to getting people to click a link or clicking play on a piece of multimedia — there is a commitment when engaging with longer media.
- Efficient People, particularly experienced web users, can accomplish tasks very quickly and consume lots of information in a short amount of time — even when glossing over information.
Lean Back
Lean back are media that are used in a more casual setting, like the living room or bedroom, where a user is more comfortable and leisurely setting. Lean back media tends to be more consumption-oriented. A choice is made early of what to consume, and then the person will feed on a steady stream of linear content.
Examples of lean back media are television, books, magazines — and to a lesser extent tablet and smartphone devices.
- Consumption Device People will choose a stream of content, like a television show or a magazine article, then consume it in a more linear fashion.
- Comfortable, Leisurely Most of the time these devices help people pass the time or relax. There isn’t as much of a goal to accomplish a task.
- Longer Attention Span Video content can be hours with a movie, and books can take many hours to read.
- Linear Most of these devices are streams of content consumed linearly from beginning to end.
Stand-up
The “stand-up” description refers to smartphones and other wearable devices. These are multifunctional and are used throughout the entire day — from the moment people wake up, until they fall asleep.
They aren’t used with great intention; people don’t make plans around their smartphone usage. They just happen to be available throughout the day to pass the time. They are also used with great utility.
The moments between moments. People use their smartphones any time they have a moment to spare through the day.
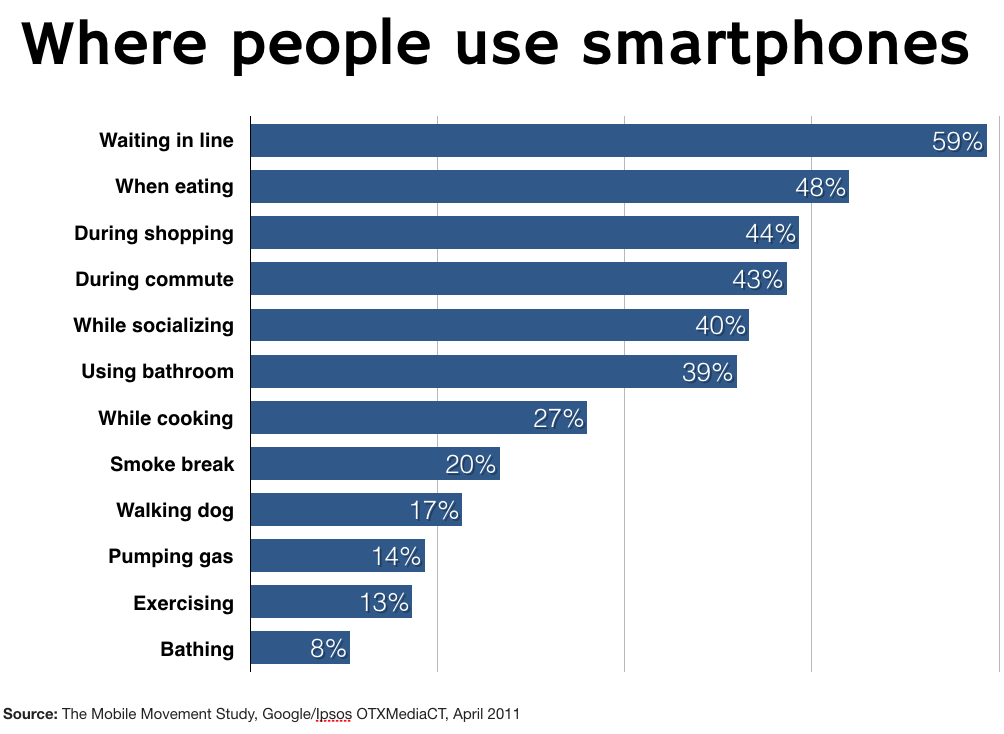
Some of the consumption characteristic vary greatly. But increasingly they are more similar to lean back devices when it comes to news.
- Consumption Device Especially in the evenings. People are reading more, watching longer video, and spending more time with these devices. It is tied heavily to how the content is designed.
- Utility Device People use these devices throughout the day, looking up information, finding directions, or to pass the time (like when waiting in line). This mean, it’s important to have quick-hit information that is stimulating and meaningful.
- A Layered Approach Many news organizations are taking a more layered approach
Choosing the best medium for the story
Understanding how the web affects journalism means thinking about how different media types (i.e. video, photo, audio, text) tell different parts of a story effectively.
| video | photography | audio | graphics | text |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Action | Emotional | Sense of a person's voice, affect | Visualizing complex stories | Descriptive |
| Sense of place | Moments | Emotion | Simplifying ideas | Background |
| Sense of character | Contemplative | Personal/Intimate | Data | History and context |
| Moments | Sense of place | Explanatory | Going places humans can't go | Informational |
| Takes you there | See how a person looks | Narrative/Linear | Location/Geography (maps) | Explanatory |
| Process | Expression | Context |